Jump to a section:
Sample types
Polymer samples for GPC analysis should be submitted to the system that matches the moiety/chemistry guidelines below.
| Mobile phase | Column | Moiety types allowed |
| THF | Styragel HR-4E | organic polymers: oligomers, epoxies, polymer additives, phenolics, unsaturated polyester, urea/formaldehyde, polyethylene glycol, ethanolamines, melamine resin |
| HFIP | PL-HFIP gel | solvent-resistant polymers: polyester, polyamides (nylon), polyethylene terephthalate (PET), poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) |
| DCB/TCB |
Moiety’s outside the guidelines above (specific for column/mobile phase types) will interact with the column itself, retaining for longer periods and appearing larger than realistic (based on the applied calibration curve). If the sample-column interaction is very strong, the molecule may become stuck and clog the column.
General preparation
- Samples should be dissolved in the same mobile phase as the chosen GPC system. For example, if THF-GPC is desired, the sample should be dissolved in tetrahydrofuran (HPLC grade, preferred).
- HPLC grade solvents will more closely match the mobile phases, resulting in fewer detector differences between sample solvent and mobile phase. HPLC grade solvents also contain fewer impurities that may interact with your polymer/sample material, interact with the column, or just complicate your analysis, in general.
- Samples are generally prepared at concentrations 1 – 2 mg/mL, 2 mg/mL maximum concentration. Smaller polymers should be prepared at higher concentrations (e.g., 2 mg/mL). Larger polymers should be prepared at lower concentrations (e.g., 1 mg/mL). The table below can be used as a guideline for concentration preparation.
- Avoid vortexing or sonicating as a way to force samples into solution. Instead, allow samples to slowly enter solution on their own. Large samples and/or highly crystalline samples will require more dissolution time. The table below can be used as a guideline for dissolution time. A minimum of 1 hour is recommended, with overnight (~12 hours) preferred. If the material’s mass is entirely unknown, start with 24 hour dissolution time and carefully check for remaining precipitation or other particulates. If solid material is still observed, extend the dissolution time by another 12 – 24 hours and check the sample again.
- After an appropriate dissolution time, the sample should be filtered at 0.1 – 0.2 μm (hydrophobic PTFE membrane).
- Samples should be clear of precipitation, dust, or any other debris.
| Molecular weight range | Concentration range (1 mg/mL ~ 0.10%) | Dissolution time |
| > 1 MDa (1,000,000) | 0.007 – 0.02% 0.25 mg/mL | 1 – 3 days |
| 500 kDa – 1 MDa | 0.02 – 0.07% 0.5 mg/mL | 12 – 24 hours |
| 100 – 500 kDa | 0.07 – 0.10% 0.5 – 1 mg/mL | 3 – 8 hours |
| 50 – 100 kDa | 0.10 – 0.13% 1 – 2 mg/mL | 1 – 4 hours |
| 10 – 50 kDa | 0.13 – 0.16% 2 – 3 mg/mL | 30 minutes |
| < 10 kDa | 0.16 – 0.20% 3 – 5 mg/mL | 30 minutes |
Calibration
Calibrants are chosen based on the most typical samples from the moiety guidelines above. However, intermolecular forces may play an important role in apparent molecular weight. A chromatogram from three example polymers are shown below. These polymers all fall within the moiety guidelines for the desired GPC analysis, and so will not interact with the column or show different retention times based on attractive/repulsive interactions with the stationary phase. All three polymers have the same nominal molecular weight; however, the average retention time and peak shape results in different apparent molecular weights. The difference in retention time or peak shape is due to the polymer’s intermolecular forces, which allows one to appear smaller or larger, leading to more or less column diffusion, respectively.
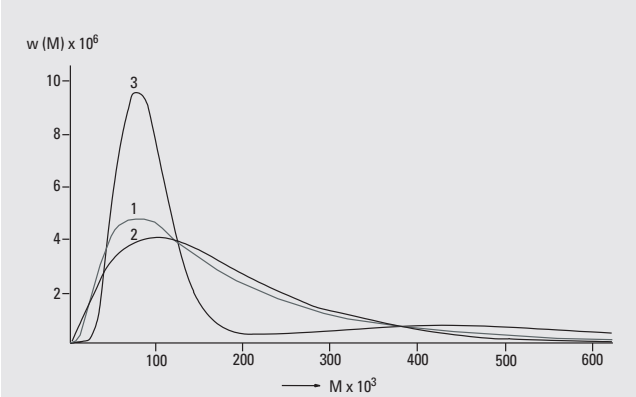
If your sample’s chemical properties are very different from the calibrant polymer’s properties (below), a different calibration may be requested.
| System/mobile phase | Calibrantion standard |
| THF | Polystyrene (PS) |
| HFIP | Poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) |
| High temperature DCB/TCB | Polystyrene (PS) |