Jump to a section:
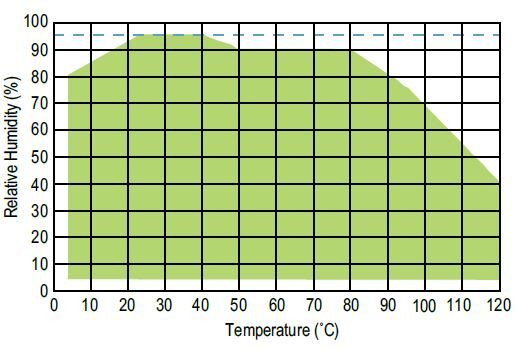
Clamps
Mettler Toledo
- Shear mode: most common for polymers to measure glassy to melt stage measurements (measures G). Ideal for gels, adhesives, high viscosity resins, elastomers, and other highly damped materials.
- Dual or Single cantilever: 3-point bending mode used for soft samples (E < 1 GPa). Good all-purpose clamp for thermoplastics, thermosets, and elastomers. Dual cantiliver mode is ideal for measuring the cure of thermosets. Make sure sample length/thickness > 10. When operating in Dual Cantilever mode, the clamp length will be ~35 mm. When operating in Single Cantilever mode, only half the clamp will be used for a clamp length of ~17.5 mm.
- 3-point bending: “Free bending” mode that eliminates clamping effects and ideal for stiff samples (E > 1 GPa). Make sure sample length/thickness > 10.
- Tension: Uniaxial deformation of thin bars, films, and fibers. Film/Fiber clamp mode necessitates thicknesses > 2 mm. Fiber clamp mode is a drill-chuck design.
- Compression: Plate clamps for low to moderate E materials, such as foams and elastomers. Useful for measuring compression or expansion, tack testing for adhesives, compression set of rubber o-rings.
- Penetration: Additional probe kit for compression plate clamps. Ideally designed for higher stiffness materials and local measurements by using smaller probes.
Samples and Mounting – Samples are typically rectangles (LxWxT) of approximately 25 mm x 6 mm x 1 mm produced in molds, but additional sizes can be accommodated, depending on clamp types (see table below). Ensure all samples have a uniform thickness with uniform lengths/widths. Use parallel cutters or sanding to ensure all dimensional imperfections are removed.
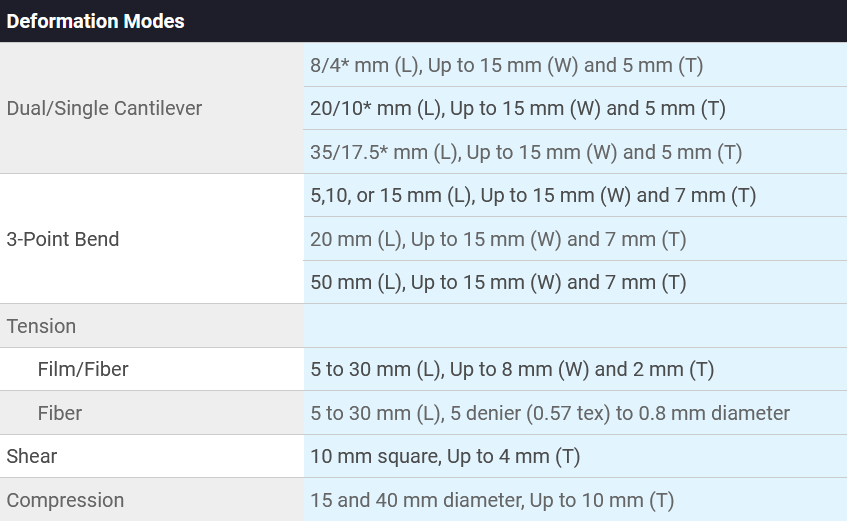
Make sure to accurately measure the sample dimensions using the caliber for width and thickness. The sample length is most accurately measured after mounting (i.e., distance between the clamps).
Place the sample in the clamp. Finger-tighten the sample while the moveable shaft is in Floating mode, ensuring the sample is straight in the clamp. Once the sample is in place, change the moveable shaft to Lock mode. Set the Torque Wrench to 8 – 10 in*lbs, sample material dependent (use the table below to determine the best torque value). Less torque may be required for thin or soft materials and torque values should be reduced so that no sample tearing is induced during tightening. Tighten the sample without pushing down on the movable shaft during tightening.
| Material properties/type | Torque value (in*lbs) |
| Stiff samples | 8 – 10 |
| Thermoplastics / Elastomers | 5 – 8 |
| Films | 2 – 3 |
Experiments
- Temperature: Temperature of relaxation transitions. Ramp of 0.05 – 3 K/min.
- glass transition temperature
- crystallization
- curing
- compatibility
- damping behavior
- Frequency: relaxation behavior
- glass transition process
- molecular interactions
- damping behavior
- Amplitude: non-linear properties
- effects of fillers
- TMA modes: static forces
- coefficients of thermal expansion
- stress/strain diagrams
- stress relaxation
- creep
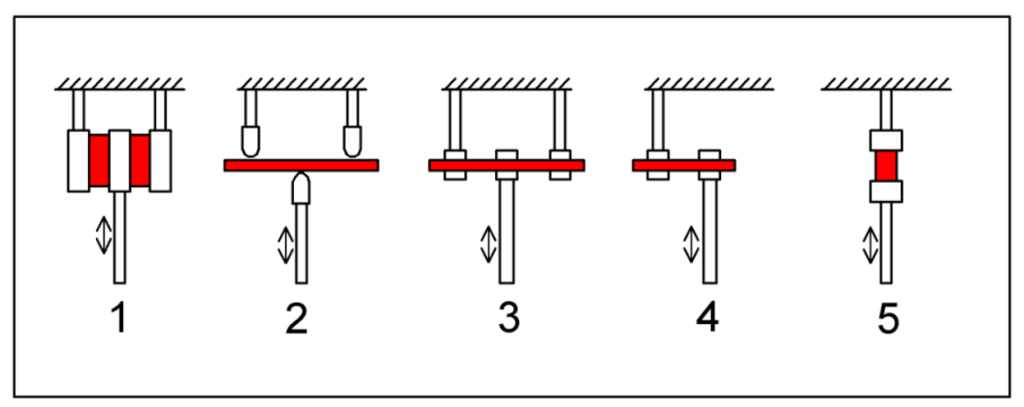
- Humidity control: viscoelastic behavior as a function of relative humidity.
- Most commonly used for tension experiments.
| Temperature range | 5 – 120 °C |
| Heating/Cooling rate | 1 °C/min (maximum) |
| Humidity ramp rate | 2% relative humidity/min (fixed) |